Only One Fifth of Global Population Achieves Sufficient Vitamin E Status
DSM Nutritional Products highlights a study published in the International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research <http://econtent.hogrefe.com/
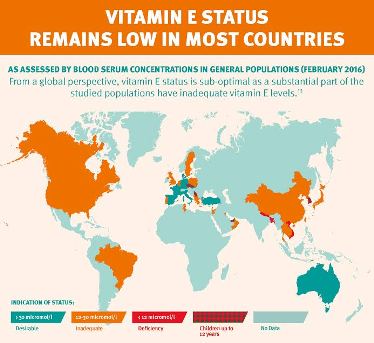 Vitamin E is an essential micronutrient that protects cell membranes from oxidative damage, including those rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). The higher the level of PUFA intake, the more vitamin E is required. This study finds vitamin E status to be alarmingly low globally. Modern changes in diet may be a contributing factor. Vitamin E status can be increased by eating more foods high in vitamin E, such as vegetable oils, green vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grain bread; fortified foods and beverages, and dietary supplements.
Vitamin E is an essential micronutrient that protects cell membranes from oxidative damage, including those rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). The higher the level of PUFA intake, the more vitamin E is required. This study finds vitamin E status to be alarmingly low globally. Modern changes in diet may be a contributing factor. Vitamin E status can be increased by eating more foods high in vitamin E, such as vegetable oils, green vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grain bread; fortified foods and beverages, and dietary supplements.
Dr. Simin Meydani, Director of Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University, comments: “This global assessment of vitamin E status – the first of its kind – is an important step to generate awareness because so many people around the world do not consume recommended amounts of vitamin E. An adequate vitamin E intake is needed to maintain the immune system, cognitive function, cardiovascular health and liver function. The findings of the publication suggest that health authorities need to dedicate more attention to the intake, status and role of vitamin E in human health.”
Applying a Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) of 15 mg/day and Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) of 12 mg/day to all populations with a minimum age of 14 years, 82% and 61% of data points were below the RDA and EAR respectively. The new paper further reveals that globally 13% of the scientific publications indicated serum concentrations below the suggested deficiency threshold concentration of 12 µmol/L, mostly in new-borns and children.
Szabolcs Péter, MD, PhD, Senior Scientist at DSM, and one of the co-authors, says: “This comprehensive review of vitamin E dietary intake and serum concentrations demonstrates that the majority of the reported intake values worldwide are below recommended levels. Similarly, it shows that a considerable proportion of the global population do not reach the proposed optimal serum concentration for vitamin E. This study should help stimulate needed research to understand the complex field of vitamin E and its impact on human health.”
The study found that vitamin E intake differed regionally. People living in the Middle East and Africa (27%) were more likely to be consuming below the RDA, but the prevalence was also relatively high in Asia Pacific (16%) and Europe (8%). Considering a threshold concentration of 30 µmol/L recommended by experts, 27% of the American, 80% of the Middle East/African, 62% of the Asian, and 19% of the European populations are below this serum value. On the other hand only 21% of the total data points included in this global review reach a desirable mean serum concentration of 30 µmol/L or higher. This can be explained by varying diets and nutrient availability across the world.
Dr. Manfred Eggersdorfer, Senior Vice President, Nutrition Science & Advocacy at DSM and Professor for Healthy Ageing at Groningen University concludes: “This review is an important step to drive awareness and education on the implications of suboptimal vitamin E status on individual as well as public health, and for the large part of the populations for which data is even lacking. There is a strong case for health authorities to dedicate more attention to the role of vitamin E in health care systems and to review recommendations”
For more information on vitamin E and the latest science, please visit DSM’s webinar channel https://www.brighttalk.com/